Introduction
In the digital age, cloud storage is indispensable. For years, Dropbox has been the default choice for individuals and businesses alike. However, convenience often comes at a cost, and a closer look at Dropbox security issues reveals a recurring cycle of challenges. From the massive 2012 hack that exposed 68 million passwords to the April 2024 breach of Dropbox Sign, the platform’s history is a case study in digital vulnerability.
For users entrusting their most sensitive documents to the cloud, these Dropbox security issues raise a critical question: Is your data actually safe with legacy cloud providers?
This article explores the history of these breaches, the root causes of major Dropbox security issues, and what the future of secure file sharing looks like in the age of quantum computing.
Analyzing the History of Dropbox Security Issues
The track record of incidents suggests that this is not a one-time problem, but a systemic one.
- 2012: A compromised employee password led to the exposure of 68 million user accounts. The Guardian reported that this massive leak stemmed from a single stolen password.
- 2024 (Dropbox Sign): Threat actors gained access to emails, phone numbers, and authentication tokens (API keys/OAuth) of Dropbox Sign users. As detailed by The Hacker News, this breach highlighted significant vulnerabilities in the digital signature platform.
What is alarming is not just the breaches themselves, but their scope. In the 2024 incident, even third parties who simply interacted with a document (without having an account) were affected.

Structural Risks Behind Dropbox Security Issues
It’s easy to blame “hackers,” but the issue often lies in architecture.
1. Legacy Encryption Standards
Most traditional cloud providers use standard encryption methods that were designed decades ago. While “secure” by yesterday’s standards, they are increasingly vulnerable to modern attack vectors and social engineering.
2. The Human Factor
Centralized storage systems heavily reliant on traditional password authentication are prone to human error. A single phished employee can become the gateway to millions of user files.
How to Mitigate Dropbox Security Issues with Quantum-Safe Tech
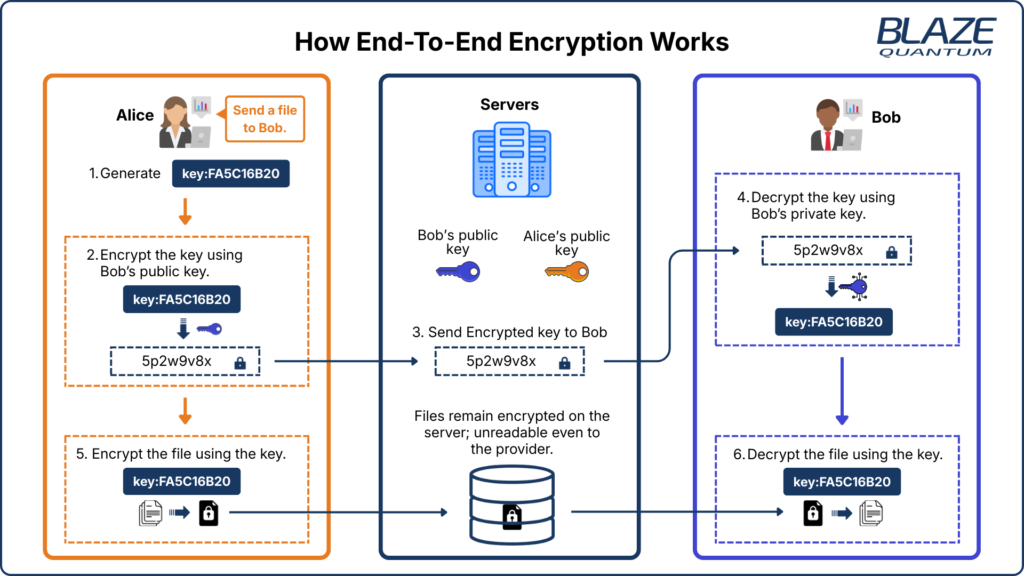
To truly secure sensitive data, we need to move from “reactive” security (patching leaks) to “proactive” architecture. This starts with End-to-End Encryption (E2EE).
1. The Immediate Fix: End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
In the Dropbox Sign breach, hackers stole a key that allowed them to read the database. If that data had been End-to-End Encrypted, even that stolen key would have been useless.
- How it works: Data is encrypted on your device before it ever leaves. Only you hold the decryption key.
- The Result: Even if the service provider is hacked (like Dropbox), the attackers only see scrambled code, not your confidential files.
2. The Future Shield: Quantum-Safe Security
While E2EE solves the immediate threat of “provider compromise,” we must also look ahead. With the rise of Quantum Computing, traditional encryption methods (like RSA) could soon be broken in minutes. This is where Quantum-Safe technology comes in. It ensures that the encrypted data you send today cannot be cracked by the supercomputers of tomorrow (preventing “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” attacks).
How BLAZE Resolves These Dropbox Security Issues
While Dropbox struggles with legacy infrastructure, next-generation platforms like BLAZE Quantum were designed to address these exact vulnerabilities. Instead of relying on outdated standards, Blaze uses Quantum-Safe Hybrid KEM [ML-KEM (Kyber-1024) + ECC-256] encryption. This ensures that your data is future-proofed against threats that don’t even exist yet.
For a deeper dive into our security architecture, read our Quantum-safe Secure Key Exchange White Paper.
Blaze combines these two powerful layers:
- True E2EE: Ensuring only you and your intended recipient can access the file.
- Quantum-Safe Cryptography: Using advanced algorithms [ML-KEM (Kyber-1024) + ECC-256] to future-proof your data.
Why consider an alternative?
- Unlimited File Transfers: Deliver your largest project files (8K videos, datasets) without the storage bloat of traditional cloud drives.
- Compliance: Ready for strict standards (ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR) where data integrity is non-negotiable.
Conclusion
The Dropbox breaches serve as a wake-up call. “Big” doesn’t always mean “secure.” As cyber threats evolve, so must our tools. Relying on legacy platforms for sensitive data is a risk that businesses can no longer afford to take.
It’s time to rethink how we share.
Ready to secure your data?
Don’t wait for the next breach news cycle. Experience true privacy and speed with BLAZE Quantum today.
Curious how we stack up against other giants? Check out our comparison: WeTransfer vs BLAZE Quantum.





